
Requirements for coating thickness #
Based on the Steel thickness of the steel, the coating thickness need to be changed.
Hot dip galvanizing coatings thickness are measured in microns . Micron is a SI Unit represented by the Greek symbol μm, which signifies one thousandth of a millimeter.
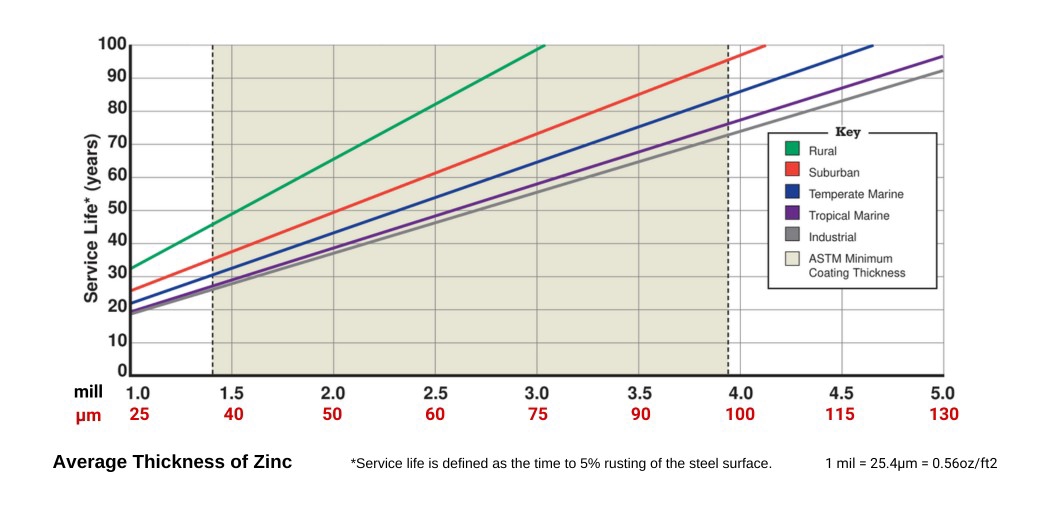
Chart based on American Galvanizers Association. Above chart is based on macroscopic environmental data and, thus, may vary from the actual corrosion rate observed, due to site-specific environmental conditions.
Generally, the thicker the steel, the thicker the zinc coating and the longer the lifespan of the protection. Silicon in steel makes zinc more reactive, so a thicker galvanized coating is needed if the steel alloy contains higher silicon.
Life time of zinc coating #
Life time of zinc coating in different corrosion categories
| Steel thickness mm | (Local coating thickness) Mean thickness µm | C4 (years) | C5 (years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel < 1.5 mm | (35) 45 | 11-21 | 5-11 |
| Steel ≥ 1.5 - ≤ 3 mm | (45) 55 | 13-26 | 6-13 |
| Steel > 3 - ≤ 6 mm | (55) 70 | 17-33 | 8-17 |
| Steel > 6 mm | (70) 85 | 20-40 | 10-20 |
| Castings ≥ 6 mm | (70) 80 | 19-38 | 10-19 |
| Castings < 6 mm | (60) 70 | 17-33 | 8-17 |
Typical corrosion environments according to EN ISO 12944-2.
- C1 - Very low : Buildings with clean atmospheres: offices, shops, schools, hotels.
- C2 - Low : Buildings where condensation may occur e.g. depots, sports, halls, rural areas.
- C3 - Middle : High humidity locations e.g. food-processing plants, laundries, breweries and dairies.
- C4 - High : Industrial areas and coastal areas with moderate salinity.
- C5 - Very high : Coastal and offshore areas with high salinity.
Time to First Maintenance #
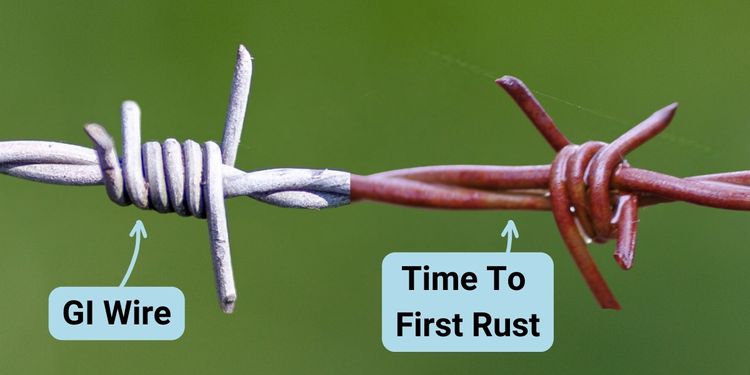
Time to First Maintenance (TFM): A galvanized steel structure will need its first maintenance when rust starts to show on 5% of its surface. This doesn’t mean that the structure is compromised, but it’s a sign that it’s time to take care of it before it gets worse.
TFM varies by thickness of the coating of zinc put on the steel during the galvanizing process and by the severity of pollution in the atmosphere to which the galvanized steel is exposed.

Factors affecting Life Span of G.I. Coatings #
Water Quality #
Hot dip galvanizing requires a minimum zinc deposit to meet standards, but increase deposit based on water quality and product life expectancy. Conduct corrosion study to determine zinc needed for desired protection.
For example, if the steel will be exposed to seawater, the user will need to increase the zinc deposit thickness, compared to freshwater exposure. This is because seawater is more corrosive than freshwater. Additionally, if the steel is expected to have a longer life expectancy, the zinc coating thickness needs to be increased.
It is also important to calculate the amount of zinc required for both the inside and outside of steel structures (e.g., steel pipes and hollow sections), as the zinc coating can corrode at different rates on the inside and outside. For example, the inside of a pipe may be more exposed to corrosive water than the outside.
Cleaner Air, Longer Protection #
G.I. coating lifespan is reduced by air pollutants, such as sulfides and chlorides from vehicles, factories, and power plants. These pollutants corrode the zinc coating, making it less effective and shortening its lifespan.
Overall, water quality and expected product life expectancy should be considered when determining the amount of zinc coating (microns) needed for hot dip galvanizing.
If you need a durable and affordable construction material that will last for decades, choose galvanized steel. It is the longest-lasting steel for your construction and fabrication needs.
Reference #
- IS 4759 : 1996 Hot-Dip Zinc Coatings On Structural Steel And Other Allied Products
- IS 4736 : 1986 Hot-dip Zinc Coatings on Mild Steel Tubes
- ASTM A123 Standard Specification for Zinc (Hot-Dip Galvanized) Coatings on Iron and Steel Products
- ISO 1461:2022 Hot dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles








